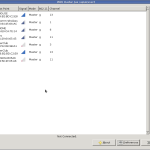
The WIFI Radar application for Linux is used to perform a wireless site survey to determine the signal strength of a wireless network that you are deploying at a particular site. This application makes a survey of wireless signal strength very easy indeed. The SSID/MAC address of the access point is shown, as well as signal strength in a bar graph. The mode, 802.11 status & channel is displayed for easy reading. This makes a scan for wireless access points lots of fun.
Install on Fedora like this.
yum install wifi-radar |
When the user of a machine is connected to an AP, they may use other command line tools to find out about the AP. Below is an example using the iwconfig command.
[homer@localhost Documents]$ iwconfig wlp0s29f7u3 wlp0s29f7u3 IEEE 802.11bg ESSID:"GTLHOUSE" Mode:Managed Frequency:2.472 GHz Access Point: 84:C9:B2:BD:C2:E8 Bit Rate=5.5 Mb/s Tx-Power=20 dBm Retry long limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Power Management:off Link Quality=70/70 Signal level=-31 dBm Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0 Tx excessive retries:4 Invalid misc:9 Missed beacon:0 |
Or the iwgetid command.
[homer@localhost Documents]$ iwgetid wlp0s29f7u3 ESSID:"GTLHOUSE" |
This command will list all available wireless interfaces on your Linux machine.
[homer@localhost Documents]$ iw dev phy#0 Interface wlp0s29f7u3 ifindex 5 wdev 0x1 addr e0:91:f5:23:fd:ad type managed channel 13 (2472 MHz), width: 20 MHz (no HT), center1: 2472 MHz
use the station dump parameter to get more information about the wireless network you are connected to.
[homer@localhost Documents]$ iw dev wlp0s29f7u3 station dump Station 84:c9:b2:bd:c2:e8 (on wlp0s29f7u3) inactive time: 19687 ms rx bytes: 684520 rx packets: 12269 tx bytes: 16436 tx packets: 320 tx retries: 23 tx failed: 6 signal: -31 dBm signal avg: -31 dBm tx bitrate: 11.0 MBit/s rx bitrate: 1.0 MBit/s authorized: yes authenticated: yes preamble: long WMM/WME: no MFP: no TDLS peer: no |
This tool and these useful commands should be very helpful when you are performing a wireless site survey.
fascinating dude!